Permafrost¶
Frozen Ground vs Permafrost¶
Seasonally frozen ground: freezes more than 15 days per year (The Ice Bowl)
Permafrost (permanently frozen ground): <= 0°C for at least 2 years (not necessary having water or ice!)
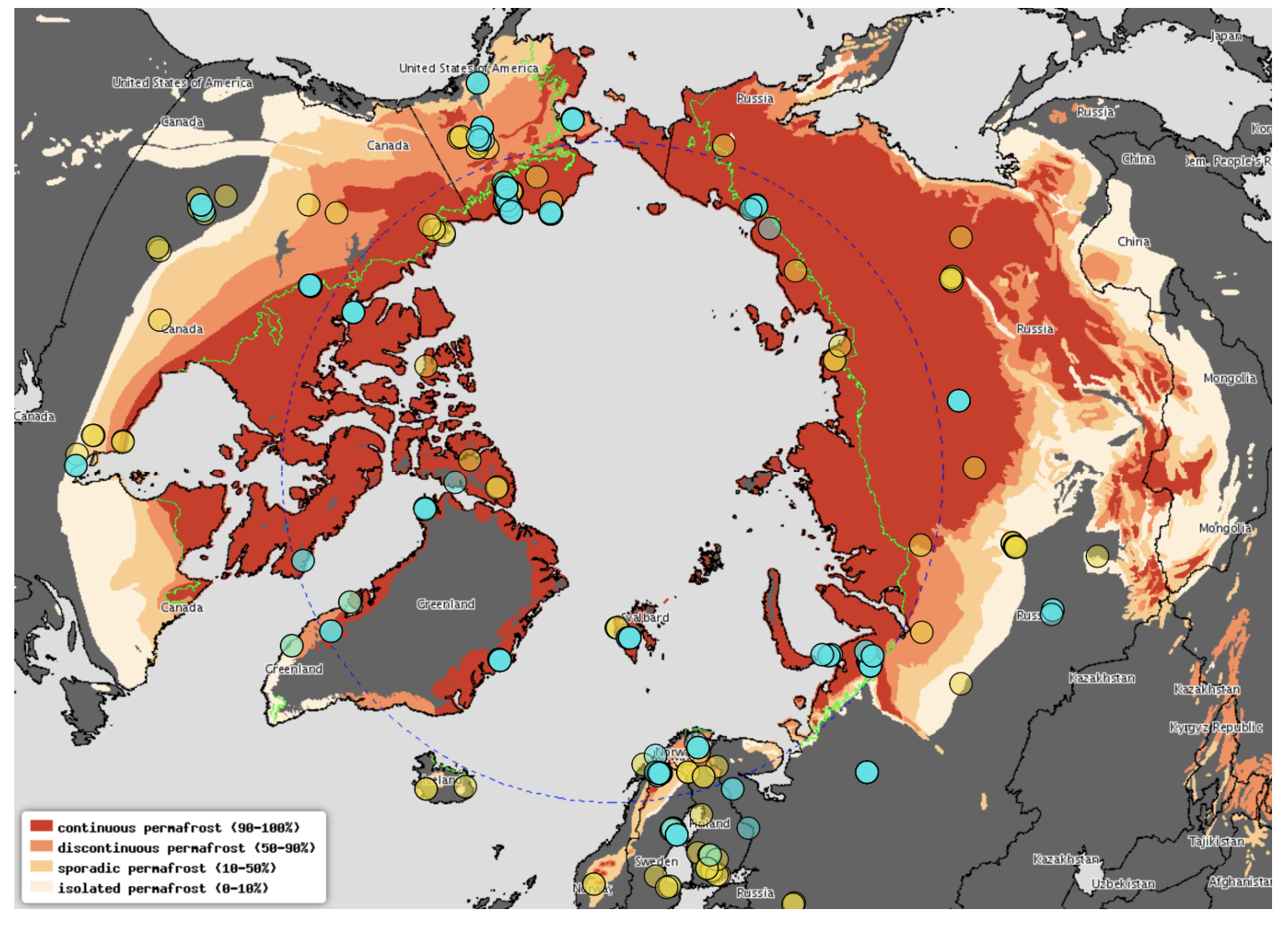
Permafrost Zones¶
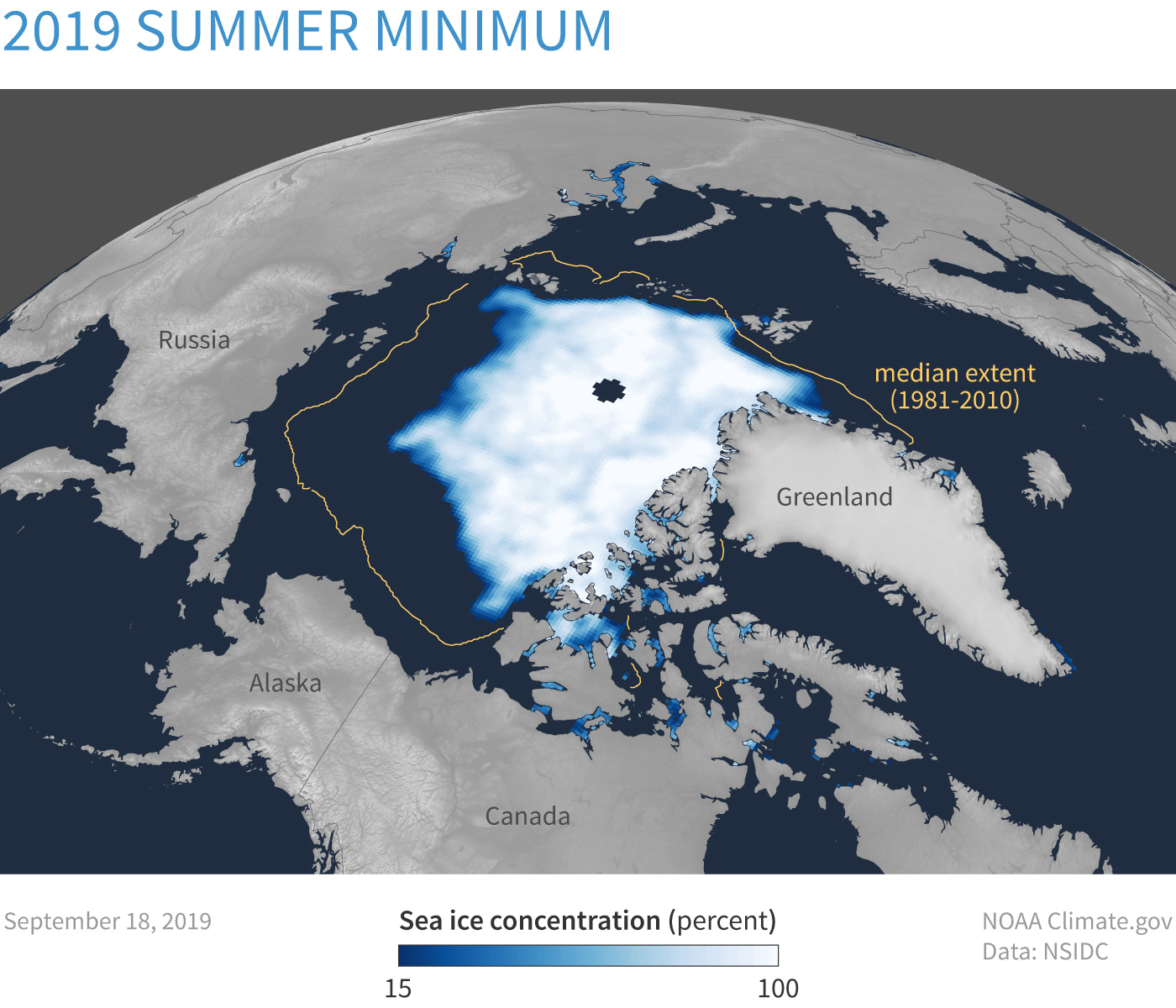
Frozen Seafloor: Subsea Permafrost¶
Factors Affect Permafrost¶
Diurnal cycle
Seasonal cycle
Geographic location
Elevation
Landscape: snow (insulator), soil type, peat, plants (evergreen trees)
Slope
Lakes and rivers: heat source, talik
Radiation
Thawing Permafrost and Climate Change¶
Satellite observations (e.g., GRACE and ICESat)
Air temperature
Moisture
Active layer
Lakes
Ecosystem
Sea level
Biological and Human Activities and Permafrost¶
Permafrost and Carbon Cycle¶
Carbon dioxide
Methane