Snow¶
Snow Characteristics¶
Colors
Crystal structure
Snow Formation¶
A general rule: snow will not form if the ground temperature is at least 5°C.
Temperature vs moisture (Antarctica’s Dry Valley!)
Most snowflakes are less than 1.3 cm.
Snow seasonality
Vertical Profile of Ground Snow¶
Daytime temperature inversion
Snow Water Equivalent¶
Definition: the thickness of water that would result from melting a given layer of snow.
25 cm of fresh snow ~= 0.25-10 cm of water.
New snow in the U.S. contains a water-to-snow ratio between 4-10%.
Snow and Weather¶
Snow forecasting remains challenging.
Follow storm tracks in boreal winter.
Blizzard and bomb cyclone
Thunder snow (summer)
Polar vortex
Snow and Vegetation¶
Wind direction
Canopy snow
Tree type
Clearings
Snowpack Energy Budget¶
Snow albedo
Latent heat of snow
Turbulent transfer
Snow and Rain Temperature¶
Snow and Water Flow¶
Lake Effect Snow¶
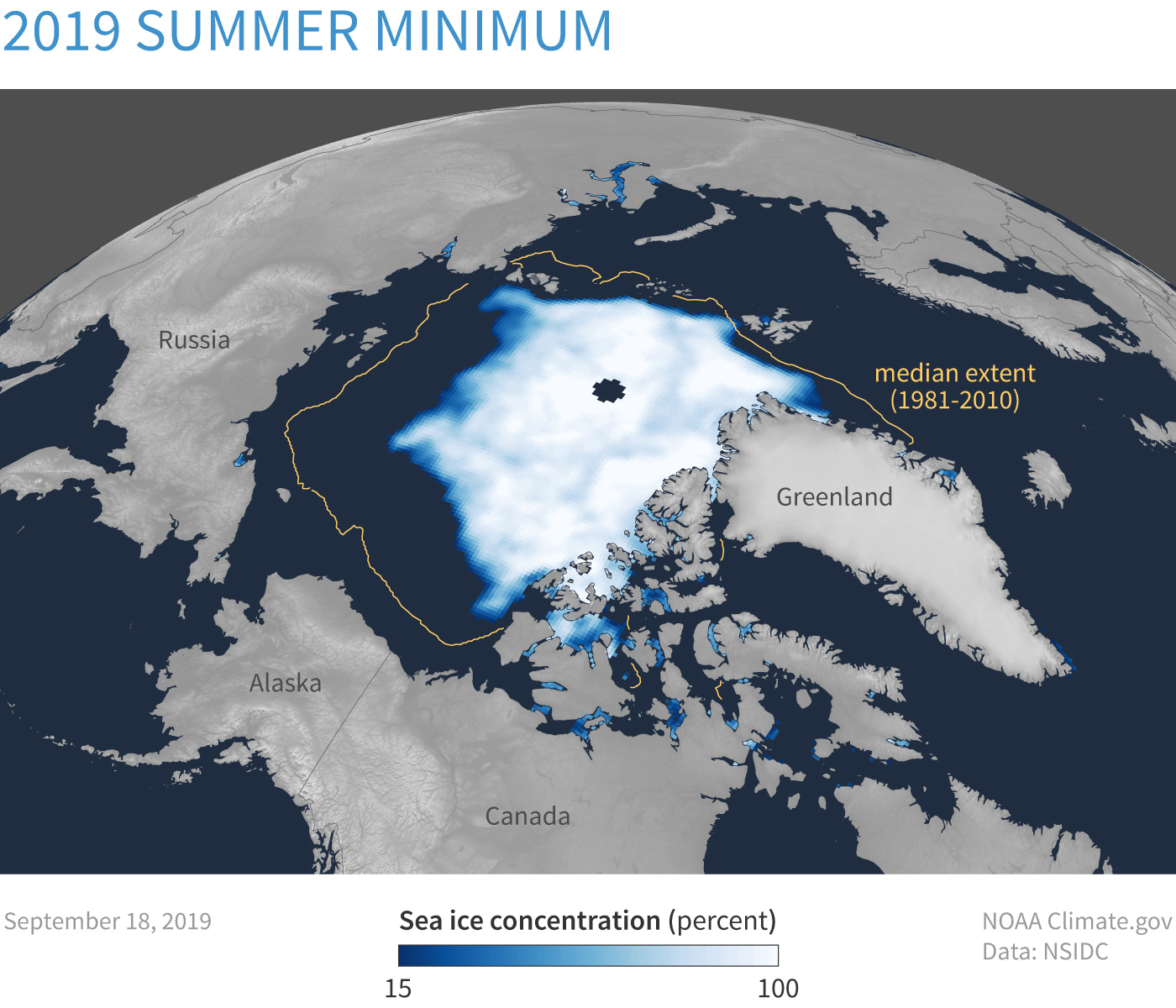
Snow and Climate Change¶
Snow trend and variability
Snow as a forcing to affect atmospheric circulation?
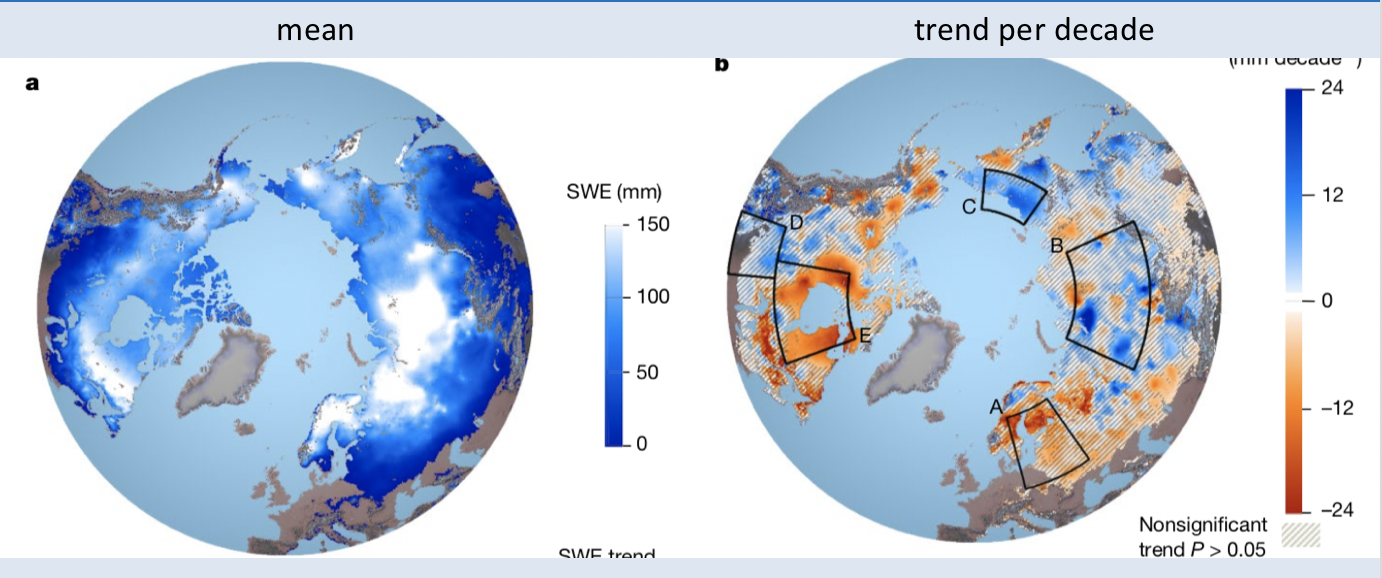
Fig. 3 March snow water equivalent and its trend (per decade). Source: Pullianinen et al. (2020)¶