Sea Ice¶
Sea-ice data illustration: individual homework assignment 10%. See more details here.
What is sea ice?¶
Sea ice is formed in the salty ocean water (-1.8°C)
Sea ice appears in Arctic and Antarctica. Sea ice can form in Bohai Bay.
Sea ice covers about 25 million square km of the Earth’s surface (about 2.5 times the area of Canada, or 15% of world’s ocean).
Classification of Sea Ice¶
By age: first-year v.s. multi-year
New ice: < 10 cm thick
Young ice: 10-30 cm
grey ice: 10-15 cm
grey-white ice: 15-30 cm
First-year ice: > 30 cm, but melt out in melting season (summer)
Multi-year ice: 2-4 m, survived melting season
Sea Ice Formation¶
Phase diagram of salt water
Ice growth process
Rough ocean: pancake ice -> rafting or ridging -> cementing or consolidation -> sheet ice
Calm ocean: grease ice -> nilas -> rafting -> congelation ice -> sheet ice
Salinity and brine
The role of waves
Multi-year Sea Ice¶
Freshwater supplies for polar expeditions.
Multi-year ice has different electromagnetic properties from first-year ice, so that satellite sensors can distinguish them.
More multi-year ice in Arctic than in Antarctica.
Sea Ice Features¶
Sea ice and melting ponds
Pancake ice
Ridged sea ice
Leads
Polynyas
Sea ice and oceanic mesoscale eddies
Lake ice
Sea Ice Thermodynamics¶
Freezing degree days (FDD in deg C).
Thickness (cm) = 1.33xFDD^0.58 (Lebedev 1938).
Snow cover slows the growth of ice.
Albedo effect (melting pond -> 0.4-0.5 and surface 0.75).
Thermodynamic equilibrium thickness (no heat transfer): 3 meters in Arctic; 1-2 meters in Antarctica.
Sea Ice Dynamics¶
Dynamics does not direct contribute to sea ice formation or reduction.
Winds
generally sea ice that drifts freely moves at 2 percent of the wind speed
sea ice surface roughness (angle).
20-40 degrees to the right in Northern Hemisphere.
Ocean currents
Coriolis force
Internal ice stress
Sea surface tilt
Sea-ice Impacts on Earth System¶
Albedo feedback
Atmospheric heat transport
Thermohaline circulation
Greenland melting
sea ice (brine effect)
Rivers (10% of world’s river discharge)
Sea-ice movements
Heat exchange
Sea Ice Gridded Data¶
Sea-ice concentration (SIC):
the amount of area covered by sea ice within one grid relative to some reference area
0-1 to 0-100%, unitless
Sea-ice area (SIA):
total area covered by sea ice -> area size times sea-ice concentration
unit in km^2 or mile^2
Sea-ice extent (SIE):
having sea ice or no sea ice in one grid -> 0 or 1
threshold: sea-ice concentration 15%
always larger than sea-ice area
unitless or unit in km^2 or mile^2
Sea-ice thickness (SIT):
freeboard
draft
unit in meter
Arctic Field Study¶
Not much reliable sea ice records before 1979.
Russian has the most sea-ice records, but when Soviet Union collapsed there’s no funding to sustain.
Beginning in September 2019, the Multidisciplinary drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate (MOSAiC) expedition sent the German research icebreaker Polarstern to the Arctic to spend a year trapped in sea ice.
Remote Sensing Measurements¶
Visible
Infrared
Passive microwave
Active microwave
Sea-Ice Modelling¶
Sea-ice Prediction¶
Methods:
heuristic model
statistical framework
dynamical framework
deep learning framework
Source of predictability:
sea-ice reemergence
atmospheric precursor
oceanic precursor
sea ice itself (?)
Changing Sea Ice in Arctic and Antarctica¶
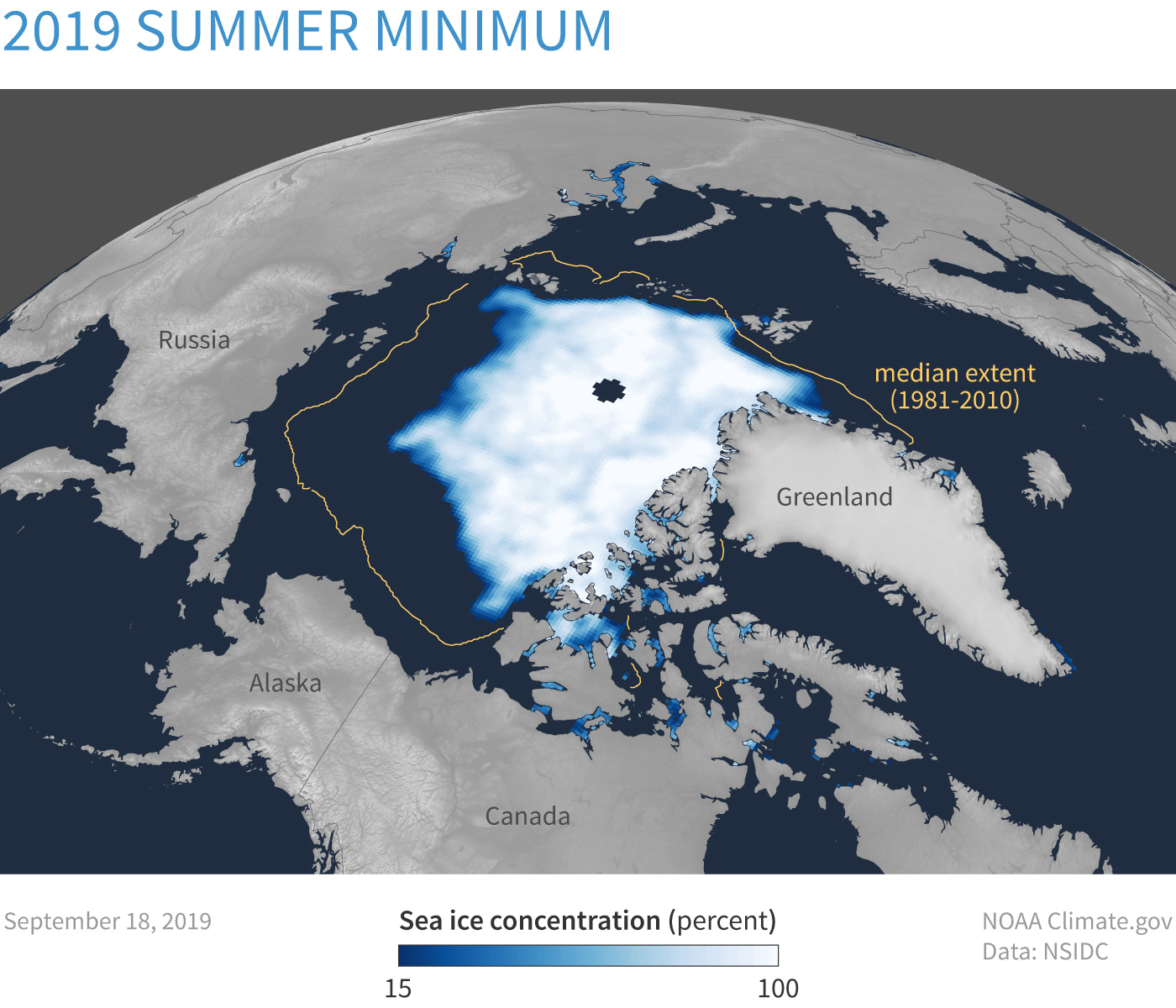
September Arctic sea ice
Arctic sea ice melt and freeze day
Riverine impact on Arctic sea ice
February Antarctica Sea Ice
Increase rather than decrease under global warming
Sea Ice in the future