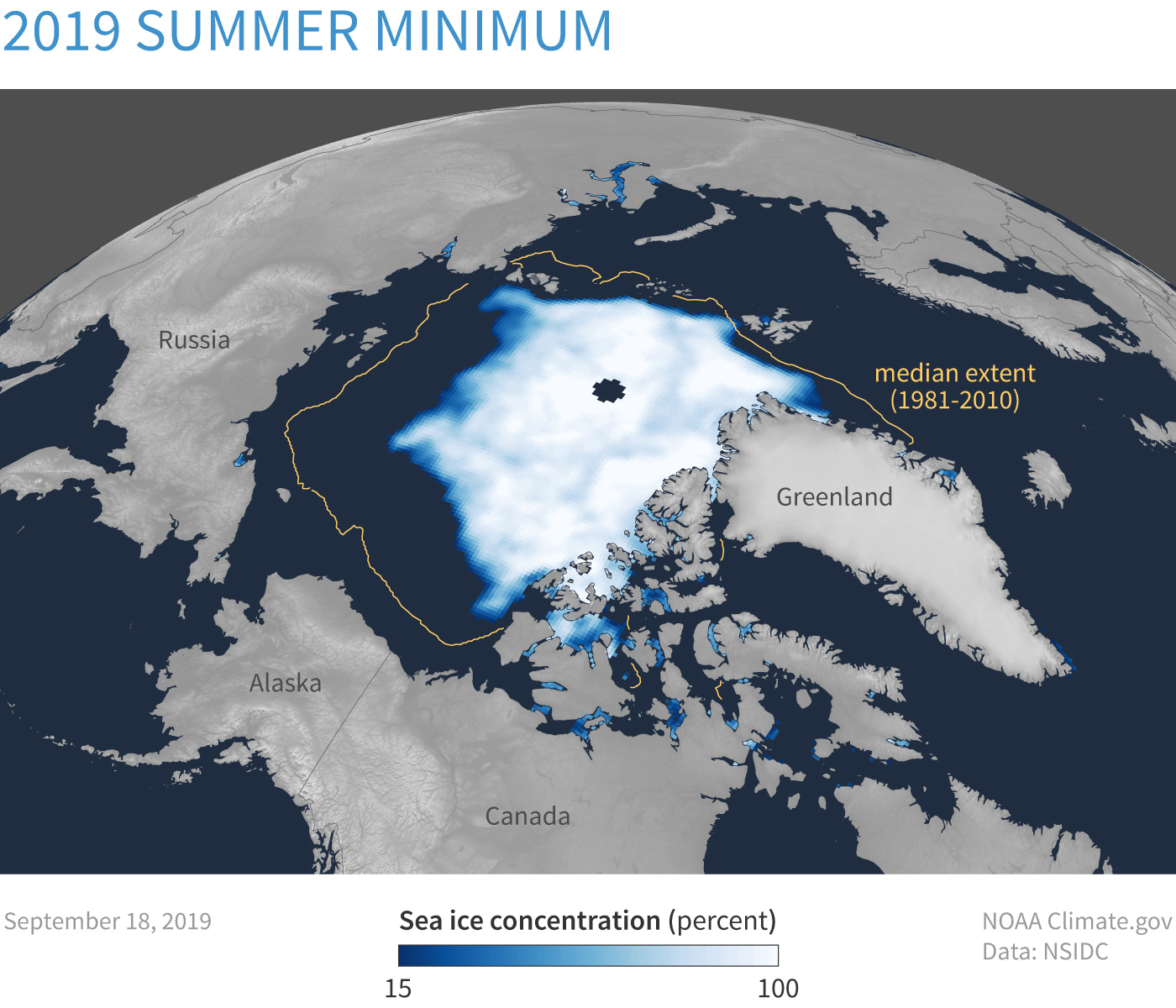
Polar Stratospheric Circulation¶
Polar Vortex & Machine Learning: individual homework assignment 10%. See more details here.
Stratospheric Polar Vortex¶
Displacement
Splitting
2020-2021 polar vortex evolution
Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW)¶
SSW and polar vortex breakdown
Days 0-30 T anomalies following SSW
“Surface Amplification” of the stratospheric signal
Definition of SSW¶
The most widely used definition of SSW is following Charlton and Polvani (2007):
“the reversal of the daily-mean zonal-mean zonal winds from westerly to easterly at 60◦ N latitude and 10 hPa from November to April (by CP07, wind reversals must be separated by 20 consecutive days of westerly winds and must return to westerly for at least 10 consecutive days prior to 30 April, to be classified as a mid-winter SSW.).“
Temperature information can be dropped because of thermal wind balance!
SSW Dynamical Frameworks¶
Large-scale planetary wave propagating upward
Planetary wave propagating upward – Charney-Drazin criterion
Baroclinic instability
Upscale cascade from synoptic-scale waves
Topography
Land-sea contrast
Planetary Wave Forcing
SSWs only happen with sufficiently strong planetary wave forcing from the troposphere.
SSWs require a pulse of anomalously strong wave forcing from the troposphere to initiate.“
Wave1 -> bottom-up
Wave2 -> top-down
Wave-mean flow interactions and dissipation
EP flux
Heat budget analysis
PV perspective
External Influences on SSWs¶
QBO
ENSO
11-year solar cycle
MJO
snow cover
sea ice
Dynamical Downward Propagation¶
Tropospheric anomalies should be proportional to stratospheric ones!
Wave driving (EP flux divergence) -> downward control (x)
Wave absorption and reflection. (x)
Baroclinic eddies (v)
Stratospheric PV anomalies (v? too weak)
Surface Signature of SSW’s Downward Influences¶
Midlatitude surface impacts
Oceanic impacts
Tropical impacts
Two-way Coupling of Troposphere and Stratosphere¶
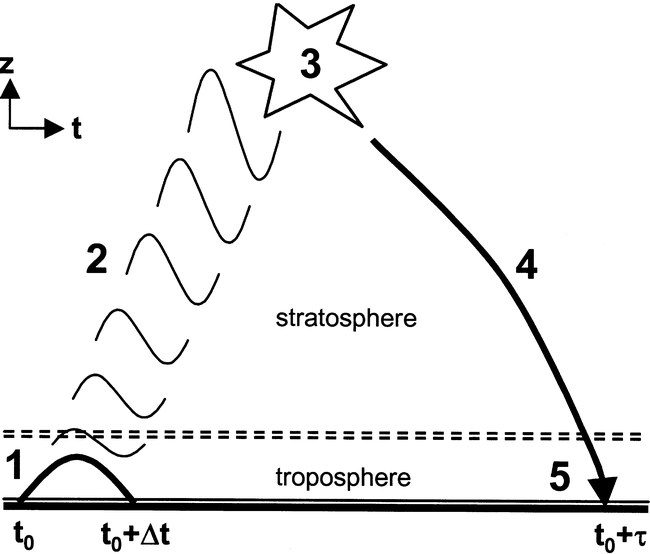
Fig. 13 Schematic illustration of the coupling events simulated in this study. (1) Forced pulse of planetary waves occurring over time Δt; (2) upward-propagating waves; (3) dissipation and breaking of waves; (4) induced downward-propagating anomalies; and (5) tropospheric response. Source: Reichler et al. (2005)¶